ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Science Videos 686 videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
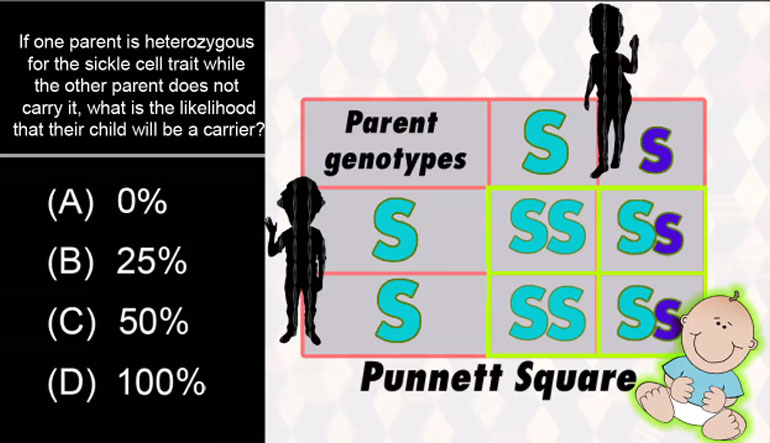
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
Molecular Genetics: DNA 466 Views
Share It!
Description:
In this video from our course on molecular genetics, learn all about animal cloning.
Transcript
- 00:14
We are here with Dr. Ruth Tennen to talk about molecular genetics, here at Shmoop Global Headquarters in Mountain View, California.
- 00:23
Dr. Ruth here is a PhD, trying to cure cancer.
- 00:26
So if you ever want to make your parents really proud of you, follow in her footsteps.
- 00:31
I can't think of much better on earth to do with your life...
- 00:36
Let's just jump right in to Lesson 1 here.
Full Transcript
- 00:38
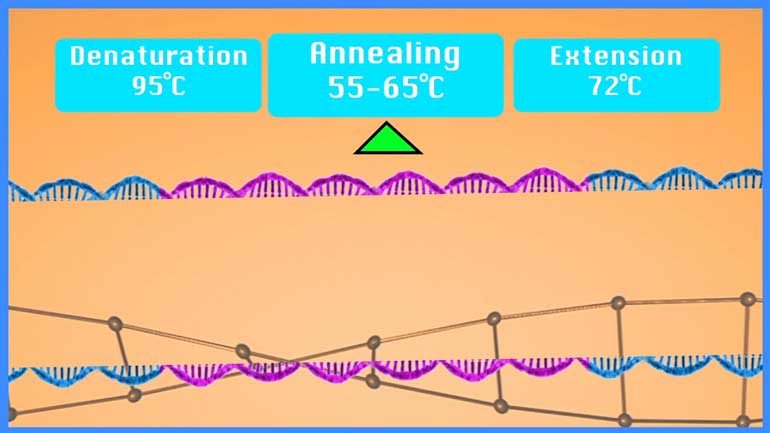
We're gonna cover genetic code and DNA/RNA structure.
- 00:43
So, Dr. Ruth, what does DNA stand for? Like...I can't even spell it...
- 00:52
So DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid.
- 00:54
So all the letters are in there somewhere.
- 00:55
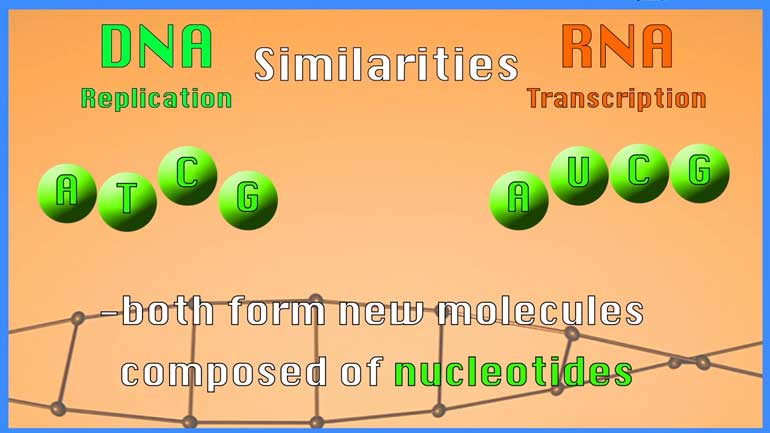
Nucleic acid is basically any polymer or any group of molecules in your cells that are composed of nucleotides.
- 01:03
So it has three parts. It has a base made of nitrogen...
- 01:05
...it has a phosphate group... and it has a sugar.
- 01:07
Okay, so we gotta back you up.
- 01:09
Polymer...that's many mer...
- 01:12
Yes, many mer. That's exactly it.
- 01:14
You have one unit of molecule, and then you string a bunch of them together. So it's a monomer to a polymer...exactly, just like beads.
- 01:22
There are a couple other five-dollar words. What is a phosphate group?
- 01:26
I'm picturing... you go to that old-style Coca-Cola stand with a hot dog and a shake...
- 01:32
So a phosphate group basically has a phosphorus and some oxygen atoms in it.
- 01:36
And it forms the backbone of the DNA, so basically it's all along the outside of the DNA molecule...
- 01:41
...and they link up together to form the chain.
- 01:44
And a nitrogen base...like...nitrogen's a molecule?
- 01:50
Nitrogen's another atom.
- 01:51
And what is its base? The ATCG is adenine, thytozine, cytosine, guanine... if I remember from high school a million years ago...
- 02:01
If you can, break down the word for us. What is "deoxy"?
- 02:05
...No longer oxy?
- 02:06
That's exactly it. It means it's missing an oxygen.
- 02:09
So basically, in the sugar molecule that's part of the nucleotide...
- 02:12
...in RNA, there's an extra oxygen compared to DNA.
- 02:15
So deoxy basically means missing an oxygen.
- 02:18
Got it. And "ribo"... that's something to do with Eve and Adam...?
- 02:24
So ribose is just a type of sugar.
- 02:26
And then nucleic...?
- 02:30
Yeah, so it's the same idea. The nucleus is made up of these nucleotides.
- 02:37
So deoxyribo tells us that it's DNA, not RNA, 'cause the sugar is missing an oxygen molecule.
- 02:47
Okay, so that's what DNA stands for. That's what comprises DNA. But what is DNA? Like, what does it do for us? How does it function...other than to confuse high school children?
- 02:59
It's actually super important. It's basically the biological blueprint that makes us who we are.
- 03:02
So it contains all our genetic information. We get half of our DNA from our mom, half from our dad.
- 03:07
And then every time our cells divide, the DNA gets split into the two cells.
- 03:11
So it kind of keeps going through all the different cells.
- 03:15
And what is its primary function? Like, walk us through the creation of the code of proteins and how that kind of builds a human being.
- 03:26
So in basic terms, you start with the DNA. You get 23 chromosomes from your mom, 23 from your dad. So that's 46 total.
- 03:33
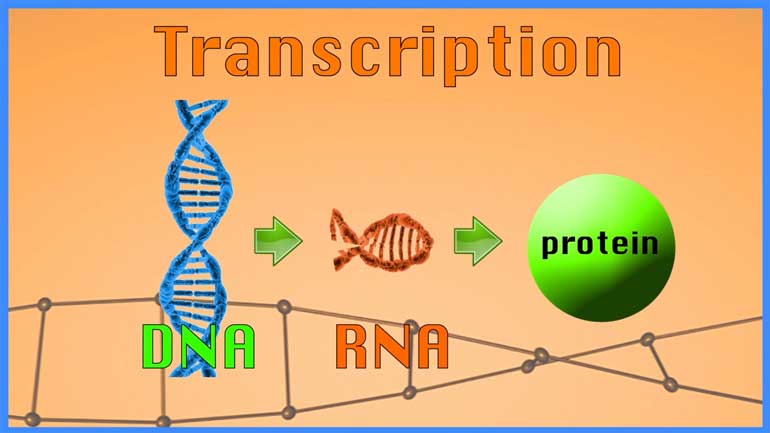
The DNA codes for an intermediate called RNA, through a process called transcription.
- 03:39
And the RNA gets turned into proteins, ultimately, and proteins are kind of the workhorses in your cells.
- 03:43
They do all the work, they form the structures in your body, they do all the enzyme processes.
- 03:47
So they give you all your traits, they can have things to do with your personality, your appearance, all sorts of things.
Related Videos
In this video, we dive beneath the sea to review the kinds of interesting animals that live in the deep blue.
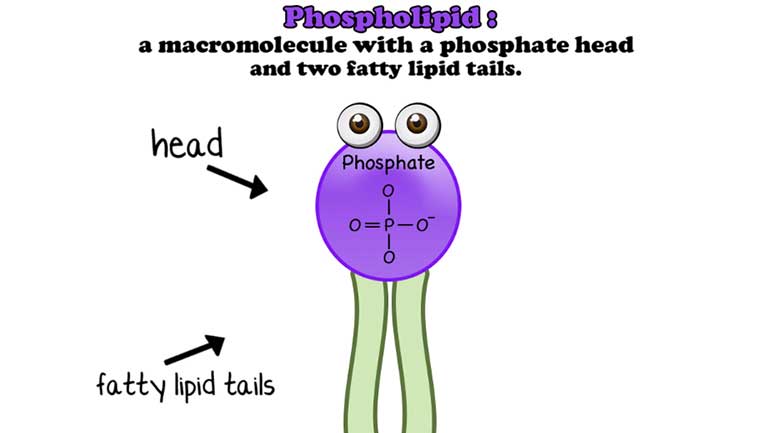
Anything that has a cell (bacteria, listen up!) has phospholipids that keep the cell contained and give it form and shape. Phospholipids protect us...
GMOs. Now that’s a scary word. Or is it? Guess it’s time to ask ourselves: WWMST? ...For those of us who don’t constantly ask ourselves “wh...