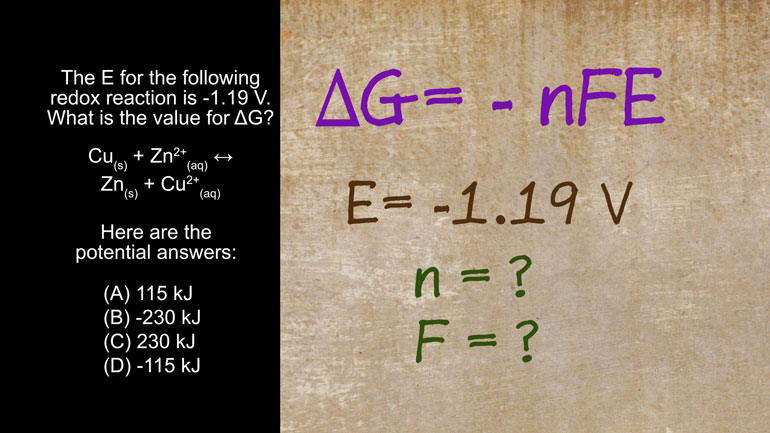ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Chemical Reaction Rates Videos 10 videos
AP® Chemistry: Reaction Rates Drill 1, Problem 1. Which of the following influences the rate of a chemical reaction?
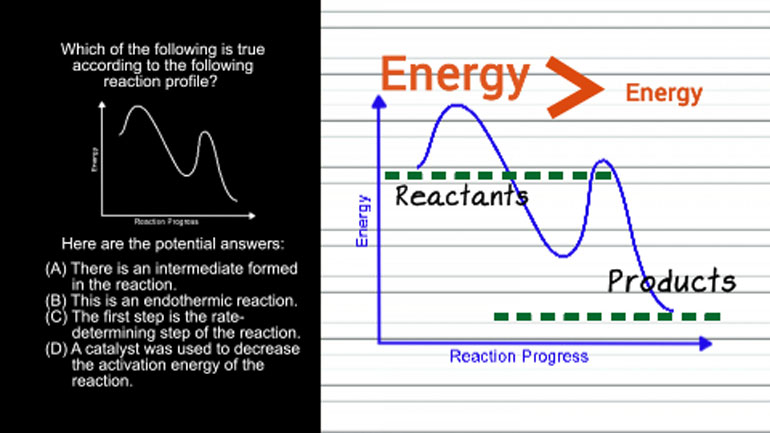
AP Chemistry 1.3 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the overall order of the reaction?
AP Chemistry 1.4 Chemical Reaction Rates. What are the correct units for a second order rate constant?
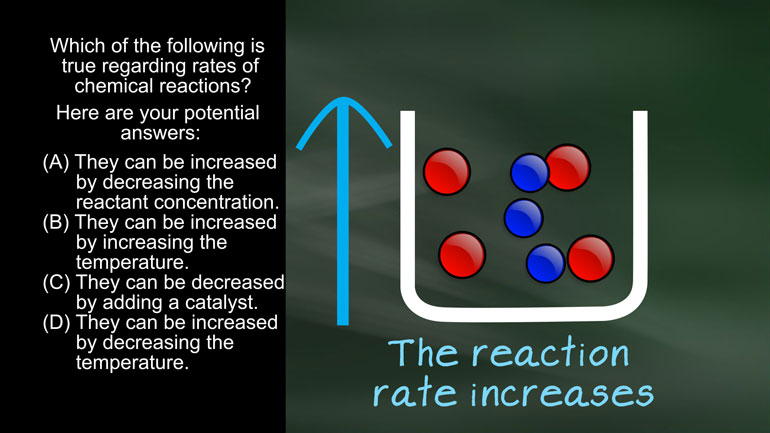
AP Chemistry 2.2 Chemical Reaction Rates 26 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Chemistry 2.2 Chemical Reaction Rates. What would happen to the reaction?
Transcript
- 00:03
Here’s your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by rockets.
- 00:06
They rock so much, they put it in the name. [Engineers working on a rocket]
- 00:10
Okay, here’s our question:
- 00:12
Nitrogen dioxide is a substance that is sometimes used in rocket fuel.
- 00:16
Nitrogen dioxide is prepared according to the following reaction, riiiiight…here….
Full Transcript
- 00:22
And the rate law for this reaction is Rate = k[NO]2[O2].
- 00:26
< The rate constant times the concentration of NO times the concentration of o2> [Rate law and reaction example]
- 00:32
What would happen to the rate of the reaction if the concentration of NO were doubled, and
- 00:37
the concentration of O2 remained the same?
- 00:40
And here are the potential answers: [mumbling]
- 00:42
Before we launch right into this problem, let’s lift off our spirits with this fuel for [Boy tied to a rocket and the rocket sets off]
- 00:48
thought.
- 00:49
Many NASA astronauts have been chemists, so if you stick with this chemistry stuff, and
- 00:54
take some time to planet all out, you too could become an astronaut…[woman astronaut holding chemical substance and it explodes]
- 00:58
And that would be out of this world.
- 00:59
Now that we’ve run out of space for these astronomically terrible puns, let’s get [woman lab worker holding two erlenmeyer flasks]
- 01:04
back to the problem.
- 01:06
We’re given the rate law for the rocket fuel synthesis reaction.
- 01:11
The rate equals the concentration of NO squared times the concentration of O2.
- 01:15
The concentration of O2 is kept constant.
- 01:18
If we double the concentration of NO into this equation, the rate will increase by a
- 01:21
factor of four, since the concentration of NO is squared in the rate law.
- 01:26
And what that means is we don't have to drag anything out and we can just go ahead and [Students yawning in a classroom]
- 01:31
tell you that the correct answer is (D), “The rate would quadruple.”
- 01:34
Phew.
- 01:35
Isn't it nice when things are simple?
- 01:36
Like going into space.
- 01:37
It's easy-peasy, right?
- 01:38
But uh…just to be on the safe side, maybe you should trade in that rocket and get your [Man lands in a store on a rocket and demands a refund for his car]
- 01:42
car back.
Related Videos
AP Chemistry 1.3 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the overall order of the reaction?
AP Chemistry 1.4 Chemical Reaction Rates. What are the correct units for a second order rate constant?
AP Chemistry 1.5 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the rate law for the reaction?
AP Chemistry 3.2 Laws of Thermodynamics. What is the value for ΔG?