ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Biology Videos 25 videos
AP Biology 4.1 Evolution. When or where is allopatric speciation likely seen?
AP Biology 2.5 Evolution. These features might be anatomically similar but could have different functions.
AP Biology 2.4 Essential Life Process Information 19 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Biology 2.4 Essential Life Process Information. What does helicase do?
Transcript
- 00:04
And here’s your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by glue.
- 00:07
Perpetually living in the shadow of super glue…what a show off. [people staring at super glue wearing a superman costume]
- 00:11
Here’s our question.
- 00:13
Helicase….what?
- 00:15
And here are the potential answers. [mumbling]
Full Transcript
- 00:20
Okay, first things first – whenever you see something ending in “ase”––that’s
- 00:26
a-s-e––in biology land, an alarm bell should go off in your head. [alarm bell sounding in a persons head]
- 00:30
…Maybe not an alarm bell.
- 00:32
Maybe just a “ding” or something. [a hand ringing a bell on someones head]
- 00:34
Either way, whenever you see something ending in “ase,” it’s probably an enzyme.
- 00:38
And usually, you can figure out what the enzyme’s job is by what comes before the “ase.” [enzyme looking for food]
- 00:44
For example, DNA polymerase adds the new bases to the DNA when the DNA is being copied. [DNA polymerase DJ'in at a club]
- 00:51
Which is basically just a fancy way of saying synthesizes, which is basically a fancy way
- 00:56
of saying we can eliminate B. Likewise, DNA ligase is the enzyme that ligates, [DNA ligase trying to stick two DNA fragments together]
- 01:01
or glues together, fragments of DNA.
- 01:04
Though we’re pretty sure a glue stick would do the trick, too.
- 01:06
So it’s not C. That leaves us with A and D.
- 01:09
The structure of DNA is a double helix. [A DNA double helix structure]
- 01:13
And if we take a look at the word in question…heli…case…
- 01:18
Probably has something to do with a helix, right?
- 01:20
Ding, ding, ding. [hand ringing a bell]
- 01:21
…Way more pleasant than an alarm, right?
- 01:24
Helicase is the enzyme that unwinds and separates DNA strands. Bit like when your mom does that with your socks.[Helicase unwinding the DNA helix and Mom unwinds socks]
- 01:31
Which means A is our answer.
- 01:33
And if you’re having trouble keeping that in mind, just remember: helicase is the enzyme
- 01:37
that unzips your genes. [Boys jeans unzip and people laugh]
- 01:39
Little forward of it, don’t you think?
Related Videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
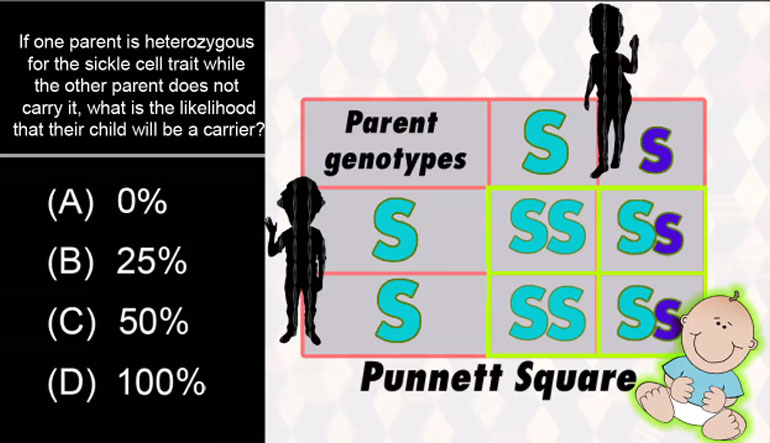
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
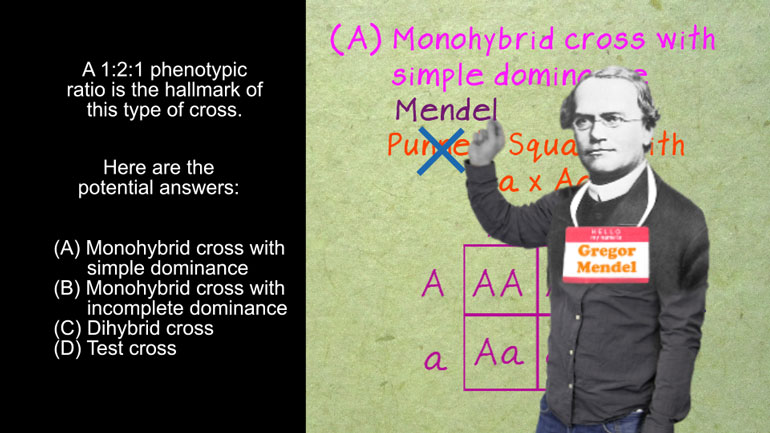
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Biology: Free Energy and Molecular Building Blocks Drill 1, Problem 1. Which statement incorrectly describes the properties of water?
AP® Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 2. What was likely the first genetic material?