ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Biology Videos 25 videos
AP Biology 4.1 Evolution. When or where is allopatric speciation likely seen?
AP Biology 2.5 Evolution. These features might be anatomically similar but could have different functions.
AP Biology 2.2 Essential Life Process Information 21 Views
Share It!
Description:
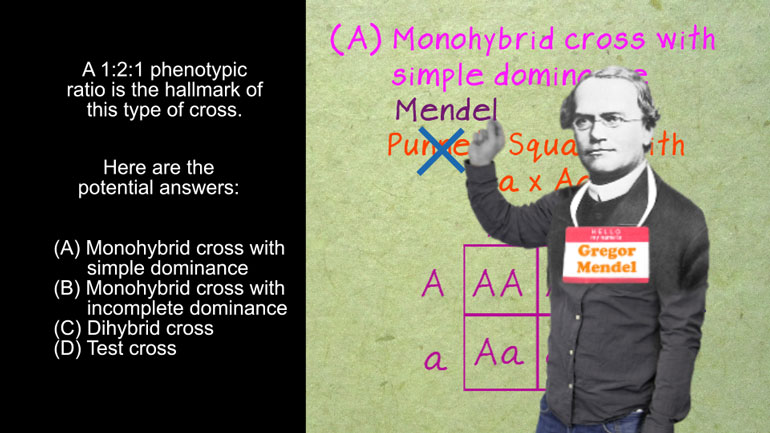
AP Biology 2.2 Essential Life Process Information. What is the probability that their son will have hemophilia?
Transcript
- 00:04
And here's your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by hemophiliacs. [red blood cells travelling quickly]
- 00:08
They're a never-ending buffet for vampires everywhere. [man in a hospital bed and vampire appears]
- 00:11
Okay, here's our question…
- 00:13
Hemophilia is an X-linked, recessive trait. A woman who is XHXh has
- 00:21
a son with a father who is XHY What is the probability that their son will
Full Transcript
- 00:27
have hemophilia? And here are our potential answers…[mumbling]
- 00:32
Okay, let's break it down… Hemophilia is an X-linked, recessive trait.
- 00:37
…What does that mean? Unfortunately, it has nothing to do with the [Two men dressed in X-men costumes]
- 00:40
X-Men. Though that sounds like a good idea for the next sequel…X-Men: Recessive Trait. [Girl watching X-Men: Recessive Trait in an empty cinema]
- 00:46
We'd watch it...just us? Anyway, X-linked means that the gene encoding
- 00:50
the trait is on the X chromosome. And remember that a recessive allele will
- 00:55
not show its phenotype if it's paired with a dominant allele.
- 00:59
So if hemophilia is X-linked and recessive, the picture looks a little more like this…
- 01:05
But what makes a sex-linked gene special, compared to all of the other genes out there? [Chromosome and gene stood together]
- 01:10
Well, besides the fact that all genes are special in their parents' eyes…
- 01:15
Sex-linked genes are exactly what the name says: sex-linked.
- 01:18
So when a mother makes her eggs, half of them will carry the diseased chromosome. [Woman with two chromosomes]
- 01:23
Now let’s take look at the father. He can either pass down a dominant allele
- 01:29
linked to the X chromosome, which would guarantee a healthy female offspring…
- 01:33
Or he could pass down a Y chromosome, guaranteeing a male offspring. [Man passing down a Y chromosome]
- 01:38
But since the hemophilia gene is on the X chromosome, a male offspring only has one [Boy opening a wrapped gift]
- 01:43
chance to get it right? And that chance comes from…?
- 01:46
Bingo. Mommy dearest. So the chances he’ll get the recessive gene
- 01:51
from his mom are… B, fifty percent.
- 01:53
That’s what makes sex-linked genes special. Because male offspring are haploid for the [Parents stood with their son]
- 01:59
X chromosome, all traits on the X chromosome, which come from the mother, are expressed. [Woman with an X chromosome]
- 02:05
Because of this, most X-linked disorders are more common in males than females.
- 02:10
Which could also explain why more of the X-Men are male than female but...don't quote us [X-Men characters in a park]
- 02:15
on that.
Related Videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
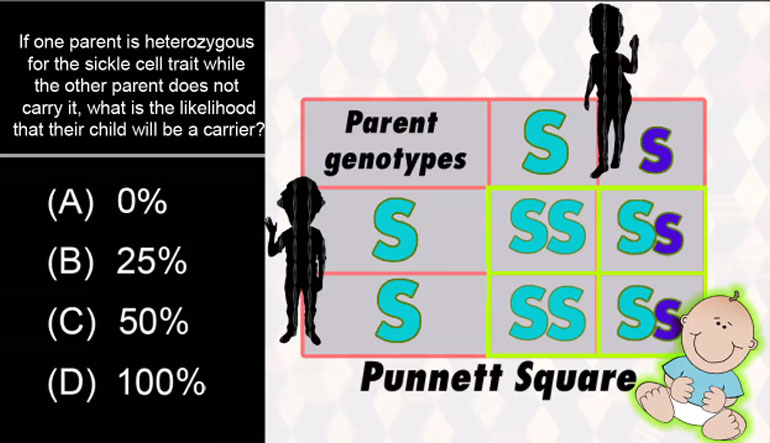
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Biology: Free Energy and Molecular Building Blocks Drill 1, Problem 1. Which statement incorrectly describes the properties of water?
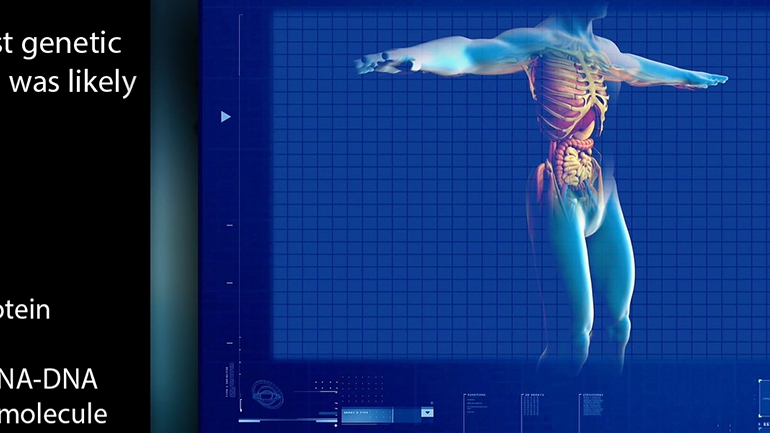
AP® Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 2. What was likely the first genetic material?