ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
U.S. History 1877-Present Videos 173 videos
Have you ever told one of your siblings to stop poking you, only to have them do something like hold their hand right in front of your face instead...
John D. Rockefeller. Greasy robber baron, or philanthropic saint? Why not both? Boy, that's a weird combination...
Today we'll learn about plans to assimilate the American Indian population after reconstruction. If you've ever seen Star Trek, you'll know that fo...
U.S. History 1877-Present 7: Foreign Policy 411 48 Views
Share It!
Description:
Today we'll learn about how the U.S. selfishly donated money to Germany to stimulate its economy. Check out the video. It turns out you totally can donate money selfishly. That one threw us for a loop too.
Transcript
- 00:04
The 1920s began with some big u.s. foreign policy moves in 1919
- 00:09
not only did we reject the League of Nations we refused to sign the Treaty of [UK flag hands over league of nations]
- 00:13
Versailles which ended World War one that one must have been quite awkward
- 00:18
didn't President Wilson give his all to get that treaty written and pass didn't [Wilson running a marathon with treaty of versailles]
- 00:23
he proudly proclaim that the treaty would show America to be the savior of
Full Transcript
- 00:28
the world while America really has never had a problem with low self-esteem but
- 00:33
for real wasn't in the League of Nations the perfect solution to war well then [League of nations appears]
- 00:37
why wouldn't our own Congress ratify the treaty join the league and save the
- 00:41
world where they all secretly Sith Lords bent on world destruction after dark [Sith Lords speaking to man]
- 00:46
we're looking to not rule on that last one out but Congress actually did have
- 00:50
some really good reasons to say no to the League of Nations one thing was that
- 00:54
the signing of the treaty would have forced the u.s. to go along with any [Person signing document and person in chains]
- 00:57
foreign action the other members approved like if the league declared war
- 01:02
the US would have to go to war so Congress role is the body that decided [Man holding gun and woman standing in the room]
- 01:06
whether the u.s. went to war or not would be erased the very thought of this
- 01:10
made the guys in Congress get all mopey if Britain and France the strongest
- 01:15
nations mer league wanted a war the u.s. would have to follow along like a little
- 01:19
puppy dog it would have no chance to evaluate the situation and suggest [Dog appears beside UK and France flag]
- 01:22
something else to America all this sounded way too much like the kind of
- 01:26
alliance that started the Great War in the first place so Congress said -
- 01:30
thanks but no thanks as for the Treaty of Versailles again America refused to
- 01:34
sign in part because we weren't totally down with Britain and France u.s. [UK crossing fingers]
- 01:38
political leaders thought that the treaty was much too harsh on Germany
- 01:42
later on in 1924 eventually President Harding signed a separate peace treaty
- 01:46
with the German led central power well the Treaty of Versailles did in
- 01:50
fact reached havoc on Germany's economy Germany was expected to make huge [UK and France flag glaring at Germany]
- 01:54
reparation payments that they just couldn't afford the German government
- 01:58
printed so much money it became worthless and the Germans literally used
- 02:01
it to fuel cooking fires showing that it's not always good to have money to [Money burning on the fire]
- 02:05
burn banker Charles Dawes who would become
- 02:08
Coolidge's vice president in 1925 came up with a plan to help
- 02:12
American banks would lend Germany 800 million marks the German currency at the
- 02:17
time to help stabilize its economy also the German National Bank would be
- 02:21
reorganized and supervised by Allied bankers and Germany's reparations [UK, Germany and France piggy banks appear]
- 02:26
payments would be restructured this was called the Dawes plan because everybody
- 02:30
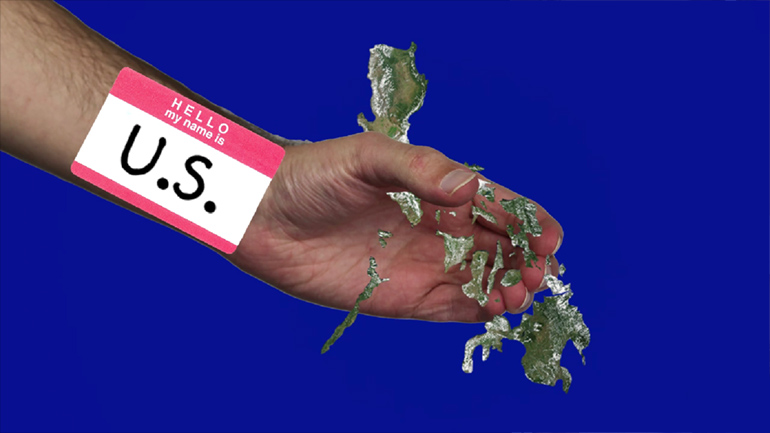
was currently too busy to come up with a more creative name why did the u.s. want
- 02:34
to help its former enemy get back on its feet because America figure that driving [US holding hand to Germany]
- 02:39
Germany into economic ruin was well just straight-up dumb first of all the Allied
- 02:43
powers would never get their money if that happened second if the German
- 02:47
economy could grow then the German government could use tax revenue to help
- 02:50
pay the reparations and you know buy stuff from us this was all in America's
- 02:55
best interest since France and Britain owed the u.s. money that they couldn't
- 02:59
pay until they caught money from Germany well the Dawes plan worked the German
- 03:03
economy stabilized and began to show moderate growth unfortunately Germany's
- 03:07
growth ended up fueling a genocidal fascist regime just a few short years [Germany holding sack of money]
- 03:12
later yeah we're talking about the Nazis who claim the money all came from evil
- 03:16
capitalist Jews trying to take over their country not that that stopped them
- 03:19
from using the resources of a stabilizing Germany to launch World War
- 03:23
two sometimes good deeds are punished and [Man dressed as Uncle Sam appears]
- 03:25
sometimes they're plain slapped in the face [Hitler slaps Uncle Sam]
Related Videos
Ever heard of a "living document"? They eat and breathe just like the rest of us! They even walk around on their own two legs. Okay, fine—maybe t...
If the Puritans had gotten their way, religion would play a much larger role in lawmaking these days. Want to know more? Watch the video for all th...
What happened between the creation of the Articles of Confederation and the ratification of the current U.S. Constitution? This video analyzes the...
The Modernists thought the world had a lot of problems, and they were intent on fixing them—or at least talking about fixing them. Unfortunately,...
This video explains Federalism and the quest for a fair balance between state and national power. It covers the progression and compromises of Fede...