ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Waves Videos 10 videos
AP Physics 2: 1.5 Waves. Which of the following explains why quantum mechanics is only applicable at the particle level?
AP Physics 2: 2.2 Waves 166 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Physics 2: 2.2 Waves. Which of the following scenarios is the least dispersive of light?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you three weeks and here's your shmoop do you
- 00:05
sure brought to you by light waves Because without him
- 00:08
the world would be a much darker place on this
- 00:11
whole video thing Well it really wouldn't work very well
- 00:13
with it All right which of the following scenarios is
Full Transcript
- 00:16
the least Disperse ihe ve of light All objects have
- 00:20
the same refractive index and hear The potential answers are
- 00:25
Art least disperse It means light's going to go through
- 00:28
and basically stay on the same path All right Well
- 00:31
let's go get a drink of water These physics things
- 00:33
or making us thirsty Important clear glass and drink through
- 00:36
a straw before we take a drink Though let's look
- 00:39
at the straw The portion of the straw that's under
- 00:42
water looks like it's in a different position in the
- 00:44
portion that's above water magic Well that's because the light
- 00:48
reflecting back to us from the straw under the water
- 00:50
is going through glass and water before hitting our eyes
- 00:53
Those materials bend the light so it hits our eye
- 00:57
at a different angle than the light from the upper
- 00:59
portion of the straw So it looks like the straws
- 01:01
bent or broken But when we take a sip of
- 01:04
that straw works just fine So refreshing All right When
- 01:08
light goes through a medium with a higher refractive index
- 01:10
and air which is pretty much everything the lightwaves bend
- 01:14
because the material they travel through slows them down The
- 01:18
angle of the bend depends on the type of material
- 01:21
But if the light hits the surface of something that's
- 01:23
already at an angle like a triangular prism resulting bend
- 01:28
will be larger than if it hit the surface head
- 01:30
on And the same thing happens when light exits something
- 01:34
like glass it ben's as it moves from one material
- 01:37
to the other Yeah but it's angle when it exits
- 01:40
also depends on the angle of the material Well those
- 01:44
changes in the angle of lighter called angular dispersion who
- 01:47
five dollar word since a square object has parallel sides
- 01:51
angles on entrance and exit are minimized and since it
- 01:56
also has perpendicular sides the right angles of the square
- 01:59
minimized dispersion for internally reflected light waves So the correct
- 02:04
answer is d and there we have it We can
- 02:07
see the solution with our own two eyes Well kind
- 02:10
of eyes need a little help with the angle of
- 02:12
refraction there And then we left our glasses somewhere So
- 02:14
likes a bit blurry right now but we think we
- 02:17
left him over in the all right Yeah i found 00:02:21.66 --> [endTime] him
Related Videos
AP Physics 2: 1.1 Properties of Objects and Systems. What is the magnitude and direction of the conventional current in this wire?
AP Physics 2: 1.5 Properties of Objects and Systems. According to the Bohr's model of the atom, which of the following are true?
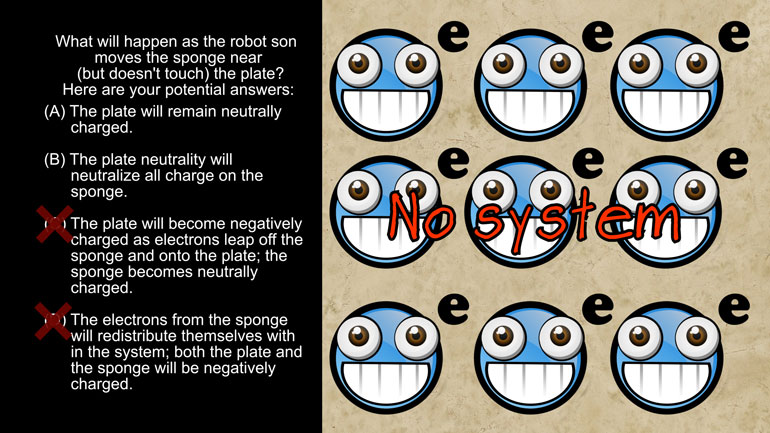
AP Physics 2: 2.2 Properties of Objects and Systems. What will happen as the robot son moves the sponge near (but doesn't touch) the plate?
AP Physics 2: 2.4 Properties of Objects and Systems. How could you show the carnival barker an emission spectrum?