ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
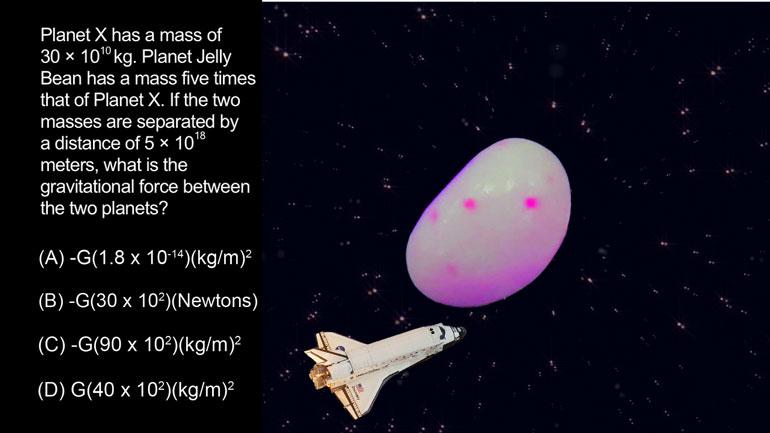
AP Physics 1 Videos 86 videos
AP Physics 1: 2.5 Changes and Conservation Law. At what point(s) in this situation is energy lost in any form?
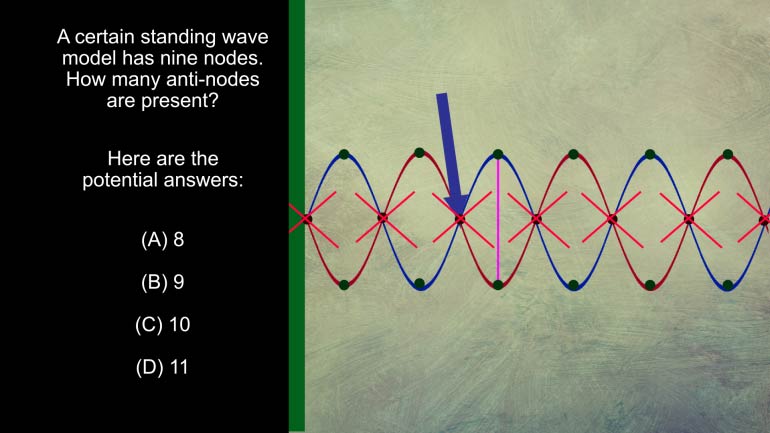
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Waves. Which of the following is technically true for Max as he stands at the edge of oblivion?
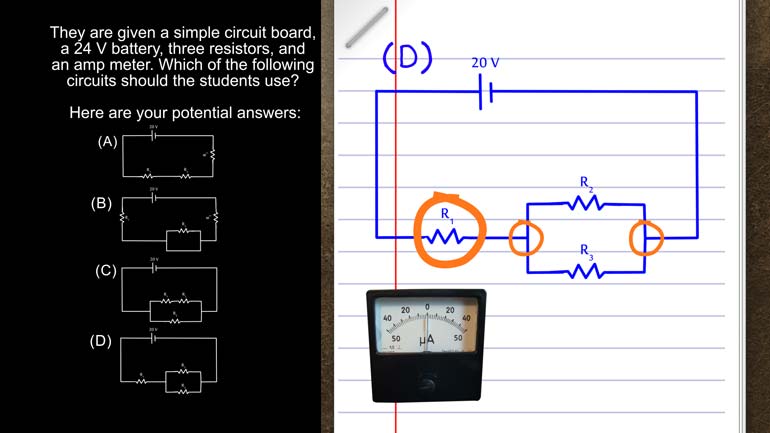
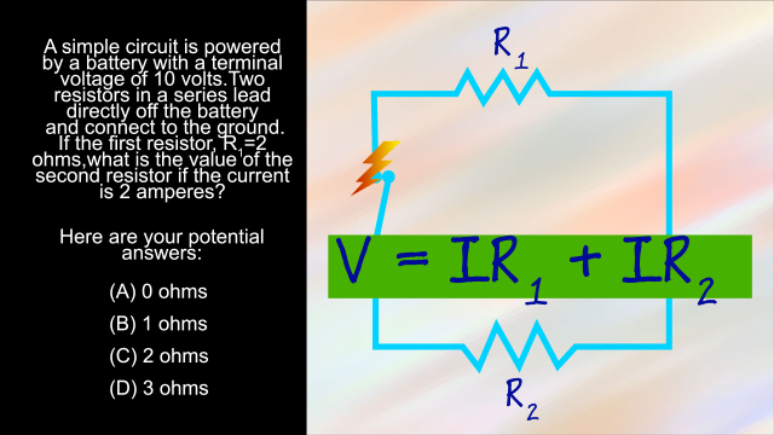
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Find the current across R2.
AP Physics 1: 3.1 Changes and Conservation Laws 196 Views
Share It!
Description:
If you bang your head against a moving wall while studying physics, and your head sticks to the wall and keeps moving, what is the combined velocity of the wall and your sad, over-taxed head?
Transcript
- 00:03
All right well here's your Shmoop du jour brought to you by collisions [Two cars collide with each other]
- 00:06
physicists are always dealing with collisions sometimes that collision is
- 00:10
their head colliding with a wall over and over again trust me i have been there a [Physicist repeatedly banging his head on a chalkboard]
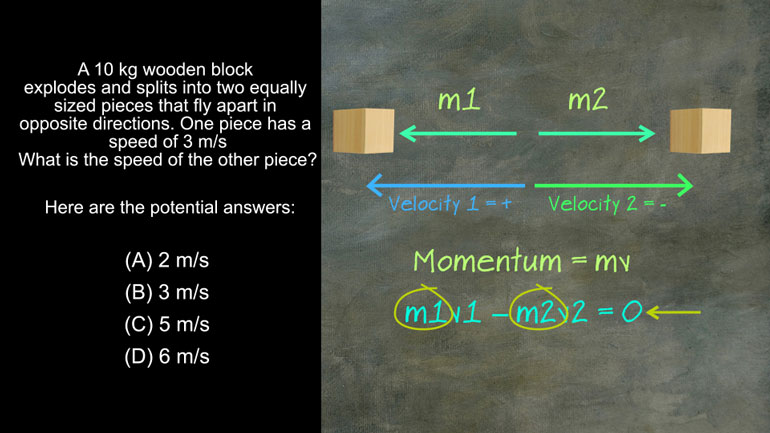
- 00:14
particle with mass 1.5 grams moves with a velocity of negative 2 meters a second
- 00:19
when it encounters a three gram particle moving to the left at a velocity of 4
Full Transcript
- 00:25
meters per second the two particles stick together and continue to move what
- 00:29
is their combined velocity here are choices [Muttering of potential answers]
- 00:33
Alright, well two particles collide stick together
- 00:37
that's right we're dealing with an inelastic collision and we're stoked [Two particles colliding and sticking together]
- 00:41
like a dream come true granted we have strange dreams there was
- 00:46
this one where we were riding a dinosaur into a tunnel and never mind actually [Two people riding on a dinosaur into a tunnel]
- 00:50
yeah, let's just get the question all right when we're dealing with an
- 00:53
inelastic collision like this we have to remember that momentum is always
- 00:57
conserved it's like there's a law about it or something so the total momentum of
- 01:02
two particles before the collision has to equal the total momentum of the
- 01:06
particles after the collision and we know that momentum equals mass times [Two particles stuck together above a definition of momentum]
- 01:11
velocity we'll call these particles one and two - that's creative right well here's
- 01:16
the equation this says that mass times velocity of particle 1 plus the mass
- 01:21
times velocity of particle 2 equals the sum of the mass of both particles times [equation for the velocity of two particles]
- 01:27
the final velocity we can flip going to decide which particle in this problem is
- 01:32
1 and which is 2 we'll say the particle with the negative velocity is numero uno
- 01:36
and now we can plug in the numbers 1.5 grams times negative 2 meters a second
- 01:41
Plus 3 grams times 4 B to the second equals 4.5 grams times final velocity
- 01:47
well solve them for final velocity gives us answer of 2 meters of seconds and the [equation filled in with the mass and velocity readings]
- 01:53
answer B is correct if you ever feel like banging your head against a wall
- 01:56
just stop take a few deep breaths and maybe take a study break because [woman stops a man from beating his head against a wall]
- 02:00
studying physics can get frustrating sometimes but studying physics with a
- 02:03
concussion, well that won't work yeah [Boy studying physics falls off chair]
Related Videos
AP Physics 1: 2.5 Changes and Conservation Law. At what point(s) in this situation is energy lost in any form?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Waves. Which of the following is technically true for Max as he stands at the edge of oblivion?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Find the current across R2.
AP Physics 1: 2.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following circuits should the students use?
AP Physics 1: 1.5 Waves. What can possibly occur when the two waves reach each other?