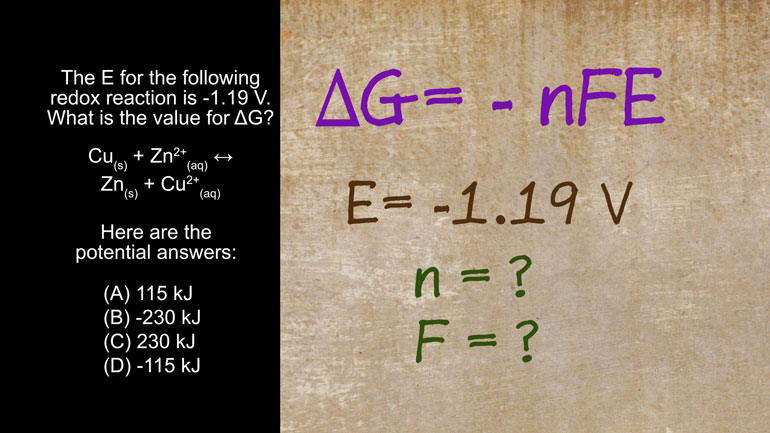ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Chemical Reaction Rates Videos 15 videos
AP® Chemistry: Reaction Rates Drill 1, Problem 1. Which of the following influences the rate of a chemical reaction?
AP Chemistry 1.3 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the overall order of the reaction?
AP Chemistry 1.4 Chemical Reaction Rates. What are the correct units for a second order rate constant?
AP Chemistry 2.1 Chemical Reaction Rates 10 Views
Share It!
Description:
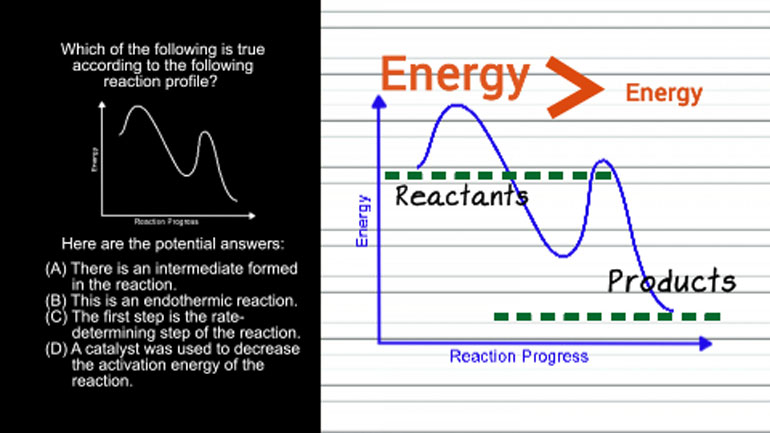
AP Chemistry 2.1 Chemical Reaction Rates. Which of the following is true according to the reaction profile?
Transcript
- 00:04
And here’s your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by humps, also known as “lovely science [Camel appears in a desert]
- 00:09
lumps.”
- 00:10
Okay, here’s our question:
- 00:11
Which of the following is true according to the following reaction profile?
- 00:14
Full Transcript
- 00:15
And here are your potential answers: Okay, so though it may just look like a random [Boy drawing]
- 00:22
squiggle a kindergartener drew, what you’re looking at is actually our reaction profile
- 00:27
curve, the focus of today’s problem.
- 00:30
Figure out what the deal with this curve is and we figure out the problem.
- 00:33
If only that was the way all problems in life worked… [Woman discussing problems with a reaction curve]
- 00:36
Believe it or not, a reaction profile isn’t the side view of a reaction.
- 00:40
It’s a graphical representation of the energy pathway through a chemical reaction. [Example of a reaction profile graph]
- 00:45
The horizontal axis shows the reaction progress, which means how close the reaction is to completion.
- 00:53
Just like in a chemical reaction equation, the left side of this graph represents the
- 00:58
reactants, and the right side represents the products. [Graph showing reactants and products of a reaction]
- 01:00
So as long as you’re used to reading left-to-right, it should be pretty easy.
- 01:05
Sorry, manga enthusiasts and Hebrew-speakers.
- 01:07
Anyway, the vertical axis is the energy of the reactant and product species.
- 01:13
You can think of it as the species in this reaction riding that curve like a roller coaster [People riding a roller-coaster]
- 01:18
as they’re transformed from the reactants into the products.
- 01:21
Woo!
- 01:22
Hope you didn’t eat a big lunch.
- 01:25
Since there are two humps here, we know that the reaction occurs in two steps. [Two humps of reaction curve highlighted]
- 01:29
And that maybe the kindergartner who drew this doodle is a camel-lover.
- 01:32
Anyway, the three local minima represent the reactants, intermediates, and products.
- 01:38
Each local maximum represents a transition state.
- 01:42
So let’s dive back into those answers. [People dive into a river]
- 01:45
Is this an endothermic reaction?
- 01:47
An endothermic reaction is a reaction that absorbs energy as heat from the surroundings.
- 01:52
From the reaction profile curve, we can see that the energy of the products is lower than
- 01:56
the energy of the reactants.
- 01:59
That means that the reaction releases energy into the surroundings in the form of heat. [Exothermic reaction definition]
- 02:04
Which means two things: It’s great to take on ski trips, AND it’s
- 02:07
exothermic, not endothermic.
- 02:08
So we can give option B the cold shoulder. [Letter B zapped and frozen]
- 02:12
Is the first step of the reaction the rate-determining step?
- 02:15
Well, out of this reaction’s two steps, the rate-determining step will be the one
- 02:19
that has the highest activation energy barrier to overcome.
- 02:24
The barrier to the first step is the difference in energy between the reactants and the first
- 02:28
transition state.
- 02:30
The barrier to the second step is the difference in energy between the intermediates and the
- 02:35
second transition state.
- 02:37
In this case, the second barrier is larger, so the second step is rate-determining. [Finger points to second transition state]
- 02:40
Looks like we’ve just determined that option C is not our guy.
- 02:45
How about D?
- 02:46
Was a catalyst used to decrease the activation energy of the reaction? [Catalyst in court with a judge]
- 02:50
Well, we have no way to tell whether a catalyst was already involved in this reaction or not.
- 02:55
Not enough information, not our answer.
- 02:57
So that means that A - “There is an intermediate formed in the reaction,” is the correct
- 03:04
answer.
- 03:05
We figured that out like a minute ago, but it’s good to consider the other options
- 03:07
just to be sure.
- 03:08
Well…that and we didn't have any other cool plans for today, and we figured we'd force [Two guys sitting on a sofa]
- 03:11
you to spend more time with us.
- 03:12
That's what friends do, right?
- 03:13
…Right?
Related Videos
AP Chemistry 1.3 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the overall order of the reaction?
AP Chemistry 1.4 Chemical Reaction Rates. What are the correct units for a second order rate constant?
AP Chemistry 1.5 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the rate law for the reaction?
AP Chemistry 3.2 Laws of Thermodynamics. What is the value for ΔG?